Please read the previous section first, as this also covers some command line usage. For a full list of commands and usage, see here.
To drop into a command shell press [c] if a boot menu is displayed – this is useful for debugging menu.lst entries. As stated earlier, if the configuration file is not found a command shell is loaded by default.
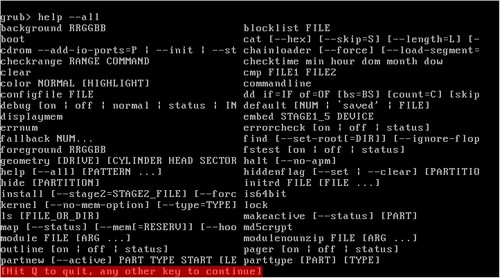
To view available commands type help --all when in the command shell – this will list all commands (see figure 1. below).

For help with individual commands type help [command] – e.g. help chainloader will display chainloader command usage.
Expanding on one of the above examples, the [tab] feature provides a quick method of finding which devices are available. Typing a relevant command followed by ( [tab] (e.g. root ( , chainloader ( , etc) will list all possible completions for the devices starting with ( - basically all devices. E.g. -
By adding a (unique) tag/marker file to the root of a device it is possible to use the find command to identify the name of the device as allocated via grub4dos. For example, typing find /hdd.tag will search the root of all supported partitions for the file hdd.tag and will return the name of the device containing the file - e.g. (hd0,0). If the file is present on more than one device, then the other devices will also be displayed. As reported earlier, devices are searched in the order (hd), then (cd), then (fd). Using the same method it is possible to use relative paths in menu entries by using the find --set-root command - see here.